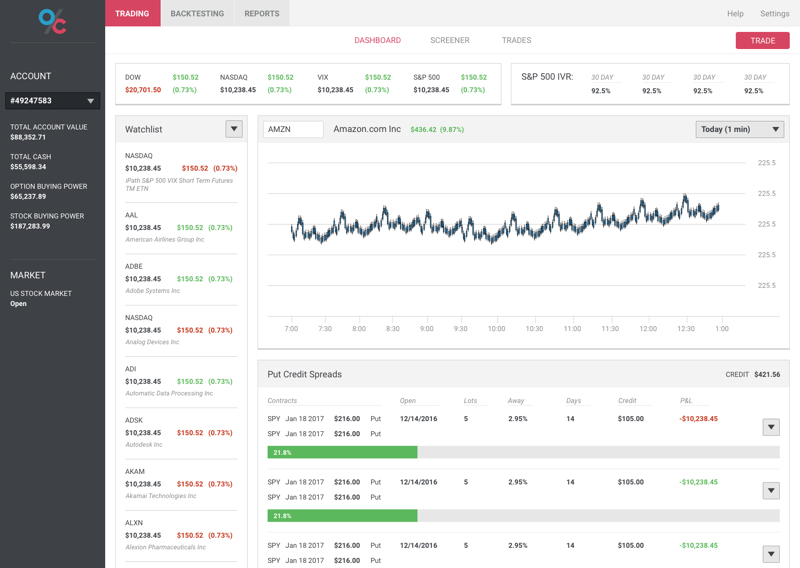
The world of options trading can be both exciting and lucrative for investors who know how to navigate its complexities. Among the many tools and strategies available to traders, the Put Call Ratio is one of the most valuable indicators. In this blog post, we will discuss what the Put Call Ratio is, how it's calculated, and how you can use it to make informed decisions in your options trading journey.
What is the Put Call Ratio?
The Put Call Ratio (PCR) is a widely used indicator that gauges the overall sentiment of the options market. It measures the number of open put options (contracts giving the owner the right to sell a security at a specific price) relative to the number of open call options (contracts granting the owner the right to buy a security at a specific price). By comparing these two types of contracts, the Put Call Ratio helps traders gauge whether the market is bearish or bullish.
The Put Call Ratio can also be used with the market as a whole. Take a look at this chart from YCharts: CBOE Equity Put/Call Ratio.
How is the Put Call Ratio calculated?
The Put Call Ratio is calculated by dividing the total number of open put options by the total number of open call options. The resulting value can range from 0 to infinity, with values greater than 1 indicating a bearish market sentiment and values less than 1 signifying a bullish sentiment. A Put Call Ratio of 1 implies that the market is neutral, with an equal number of put and call options.
PCR = (Total Open Put Options) / (Total Open Call Options)
How to use the Put Call Ratio in options trading
- Identifying market sentiment: One of the most common ways traders use the Put Call Ratio is to identify the overall market sentiment. A high Put Call Ratio (greater than 1) indicates that more traders are buying put options, which suggests a bearish market sentiment. Conversely, a low Put Call Ratio (less than 1) shows that more traders are buying call options, signaling a bullish market sentiment.
- Contrarian trading strategy:
Some traders use the Put Call Ratio as a contrarian indicator, meaning that they take a position opposite to the prevailing market sentiment. For example, if the Put Call Ratio is high, indicating a bearish sentiment, a contrarian trader may choose to buy call options, anticipating a market reversal.
- Monitoring extreme values:
Extremely high or low Put Call Ratio values can signify potential market reversals. When the Put Call Ratio reaches extreme values, it may suggest that the market is overly bearish or bullish, and a reversal could be imminent. Traders can use these extreme values as potential entry or exit points for their trades.
- Tracking historical trends:
By analyzing historical Put Call Ratio data, traders can identify patterns and trends that may help them make more informed decisions. By comparing the current Put Call Ratio with historical levels, traders can gauge whether the market is overbought or oversold and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Conclusion
The Put Call Ratio is an essential tool for options traders, as it can help determine the overall market sentiment and guide decision-making. By understanding how to calculate and interpret the Put Call Ratio, traders can gain valuable insights into market trends and potential reversals. Incorporating the Put Call Ratio into your options trading strategy can help you make more informed decisions and improve your overall success in the market.
Related Topics: Backtesting, Options Strategies, Put Call Ratio